Set It and Forget It: Automating Updates on Your Linux VPS
🔧 How to Automate Updates and Patching on Linux VPS
Managing a Linux VPS server involves routine updates and security patching. But manually handling updates every week? That’s inefficient—and risky. With the right tools and automation strategies, you can ensure your system stays secure, stable, and up to date without lifting a finger.
In this blog, we'll show you how to automate updates and patching on a Linux VPS, whether you're using Ubuntu, Debian, CentOS, or other distributions.
🛡️ Why Automated Updates Matter
Keeping your server’s OS and packages updated is essential for:
🔐 Security – Patching vulnerabilities before they’re exploited
⚙️ Stability – Keeping software versions compatible
⏱️ Efficiency – Saving time and effort for sysadmins
Neglecting updates is one of the top reasons Linux servers get compromised. Automating this task helps you focus on growing your business—not fixing avoidable issues.
🧰 Tools for Automating Updates on Linux VPS
| Distribution | Tool/Service | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Ubuntu/Debian | unattended-upgrades | Automatically install security updates |
| CentOS/RHEL | dnf-automaticoryum-cron | Apply updates at scheduled times |
| Any distro | cron+ shell script | Fully custom automation setup |
| Any distro | Configuration Managers (Ansible, Puppet) | Enterprise-grade automation |
🐧 For Ubuntu & Debian: Usingunattended-upgrades
1. Install the package
sudo apt update sudo apt install unattended-upgrades2. Enable automatic updates
sudo dpkg-reconfigure --priority=low unattended-upgrades3. Edit the config (optional)
Edit/etc/apt/apt.conf.d/50unattended-upgradesto fine-tune:
Unattended-Upgrade::Allowed-Origins { "Ubuntu focal-security"; "Ubuntu focal-updates"; };You can also enable automatic reboot if necessary:
Unattended-Upgrade::Automatic-Reboot "true";🐱 For CentOS & RHEL: Usingdnf-automaticoryum-cron
1. Install the tool
sudo dnf install dnf-automatic2. Enable the service
sudo systemctl enable --now dnf-automatic.timer3. Configure updates
Edit the config file:
sudo nano /etc/dnf/automatic.confSet:
apply_updates = yes download_updates = yesFor CentOS 7, useyum-croninstead ofdnf-automatic.
📋 Advanced: Automate with Cron & Shell Scripts
If you want full control, a simple cron job can do the trick.
Example for weekly updates:
0 3 * * 0 root apt update && apt -y upgrade >> /var/log/apt-auto.logAdd this to your crontab using:
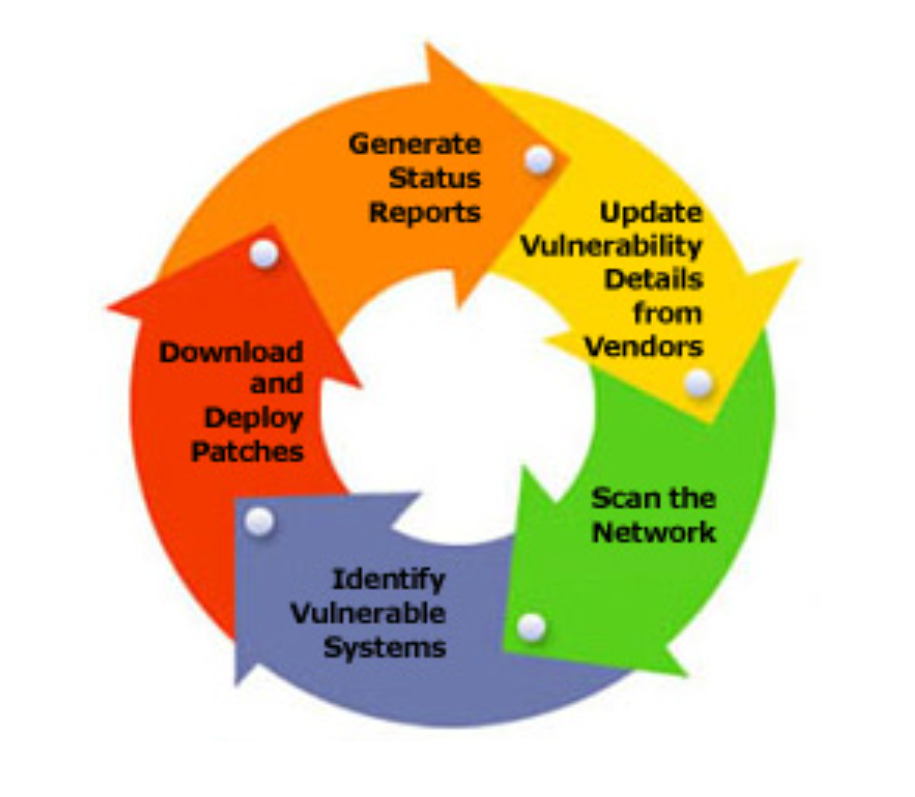
sudo crontab -e🔎 Diagram: Linux VPS Auto-Update Lifecycle
🧠 Pro Tips for Safe Automation
Enable email alerts for update reports
Whitelist critical packages to avoid accidental breakage
Test updates on a staging server before production
Use snapshots/backups before automating major version upgrades
🤖 Automate with VCCLHOSTING Linux VPS
At VCCLHOSTING, we provide Linux VPS servers pre-configured for automation. You can also:
Set up scheduled updates from the dashboard
Choose from OS templates with security patching enabled
Access monitoring and alerts for patch failures
✅ Final Thoughts
Automation doesn’t just save time—it reduces risk. Whether you’re managing one VPS or dozens, automating Linux updates is essential for performance and security.
By following the methods outlined above, you can keep your Linux server healthy, fast, and protected 24/7.
🔗 Explore More
📌 Explore VCCLHOSTING Linux VPS Plans
📌 Need Help Automating Your Server? Contact Us

Comments
Post a Comment